American beautyberry is a lovely plant that offers two wonderful display times each year. It is also known as French mulberry, sourbush, bunchberry, or purple beauty-berry. In the late spring and early summer, there are light colored lavendar flowers in small clusters along the upright stems of the plant. In fall, there is a big showing of color in the form of shiny purple fruit clusters called drupes.

American beautyberry is very important for the local wildlife; cattle enjoy the twigs and leaves in the winter and twigs in the winter. Additionally, the fruit is important for over forty types of songbirds including the American Robin, Brown Thrasher, Purple Finch, and Eastern Towhee. The drupes/clusters are eaten by armadillo, foxes, opossum, raccoon, and squirrels. Additionally, white tailed deer consume the fruit in the fall after leaves drop. They also browse the leaves in summer when highly preferred foods are not available.
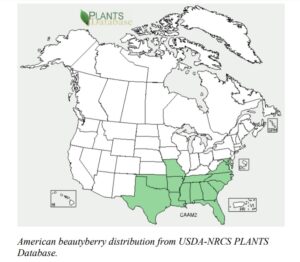 Bunchberry is also used for botanical home remedies. For instance, the roots, leaves, and branches were used by various Native American tribes for medicinal purposes to treat malarial fevers and rheumatism. The roots were used to treat dizziness, stomachaches and dysentery. Roots and berries were boiled and drunk to treat colic. The leaves can be crushed and stuffed in pockets or under hats to repel mosquitoes. Studies conducted by the Agricultural Research Service has shown two compounds – callicarpenal and intermedeol – are responsible for the repellant effect.
Bunchberry is also used for botanical home remedies. For instance, the roots, leaves, and branches were used by various Native American tribes for medicinal purposes to treat malarial fevers and rheumatism. The roots were used to treat dizziness, stomachaches and dysentery. Roots and berries were boiled and drunk to treat colic. The leaves can be crushed and stuffed in pockets or under hats to repel mosquitoes. Studies conducted by the Agricultural Research Service has shown two compounds – callicarpenal and intermedeol – are responsible for the repellant effect.